Table Of Content
This core set of 5 steps has been adopted by diverse industries and is championed by leading UX design communities including the Interaction Design Foundation. The Deliver stage is where lead prototypes are integrated with new and existing technologies. Whereas earlier stages are focused on working through ambiguity, the Deliver stage focuses on efficient execution and streamlined integration through training and technology. When building a Design Thinking team, consider the range of skills you need in order to make effective decisions during the workshop itself.
Fill in an empathy map
With that in mind, let’s consider the five key stages of the Design Thinking process in more detail. You can learn more about solution-based vs. problem-based thinking in our comprehensive guide to Design Thinking. Before we can understand the Design Thinking process, it’s important to get to grips with the ideology behind it—that is, Design Thinking.
Traits that are common across design thinking processes:
But now, as digitization drives more frequent and faster disruptions, users demand a dynamic mix of product and service. Emphasis has shifted firmly away from features and functions toward purpose, lifestyle, and simplicity of use. While a journey map captures the high-level experience of the Customer in the operational value stream, product features manage the specific deliverables that fulfill a stakeholder’s need. Features are commonly described through a features and benefits (FAB) matrix, using short phrases that provide context and a benefit hypothesis. Design thinking, however, promotes switching the order of the FAB to a benefit-feature matrix.

User-centricity and empathy
Gallery walks are most often used to pressure test working user personas, with one large poster dedicated to visualizing each user type. Gallery walks are an engaging way to share detailed results discovered during the Research or Empathy steps. They are intended to replicate the thoughtful experience of browsing in an art gallery, and participants are given worksheets or encouraged to record what stood out or surprised them. Develop a bird’s eye view of one user persona that encompasses all the important touch points relevant to your solution over time. You can (and should!) still collect user insights during tests—view session recordings, heatmaps, and even ask users for feedback when they’re in an A/B test variation.
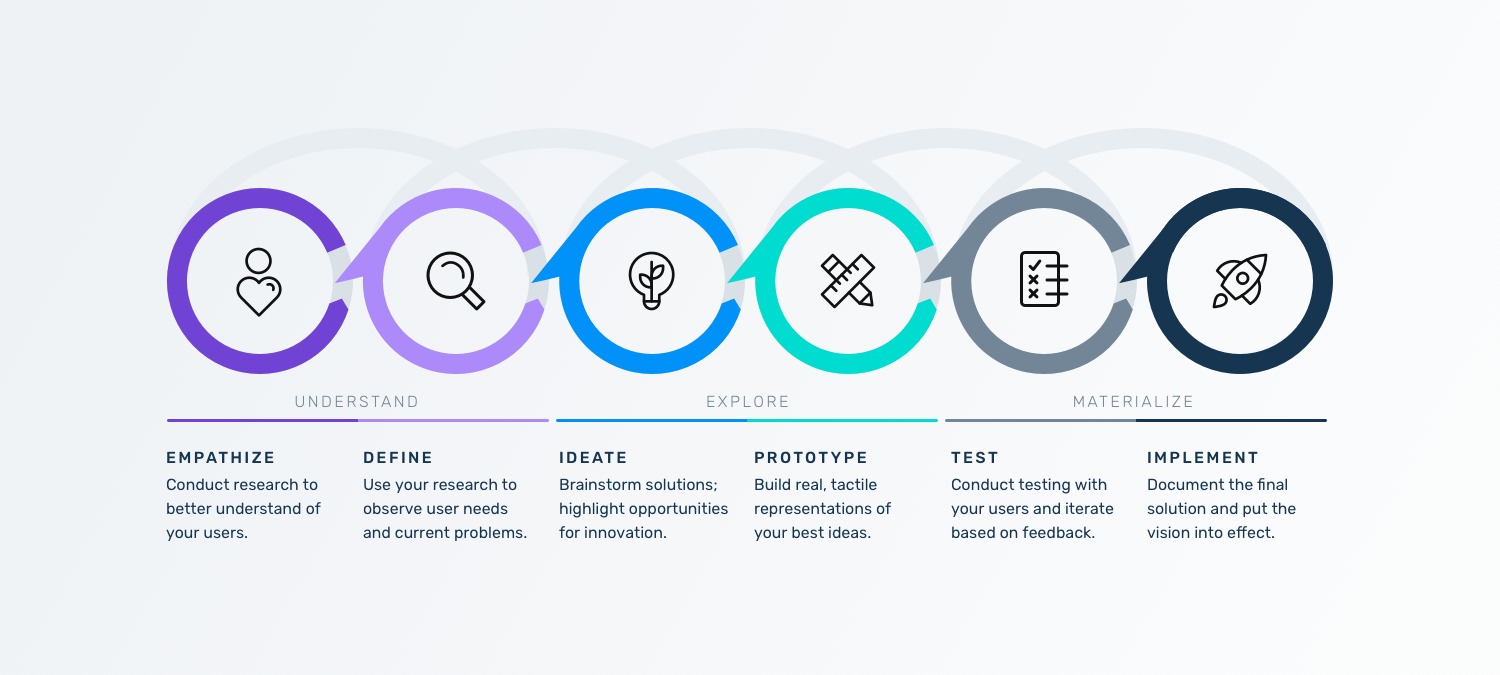
The design thinking framework: five key steps
Since these changes were made, the list of candidates has continued to grow. Now, when people arrive at the page to endorse a candidate, they clearly see a list of candidates with links to endorse them, and it’s obvious what to do next. After journalists spoke to some of these people and discovered that they were accidentally campaigning, Digital Iceland quickly redesigned the page and created a separate one for registering to collect endorsements. Stanford d.school provides three design-thinking framework challenges you can try in your class! Click on the image above to find out more, or you can download the pdf's here. The team should then collaboratively discuss and evaluate each idea ready for the next step.
IBM's Got a Plan to Bring Design Thinking to Big Business - WIRED
IBM's Got a Plan to Bring Design Thinking to Big Business.
Posted: Thu, 21 Jan 2016 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Stanford d.school
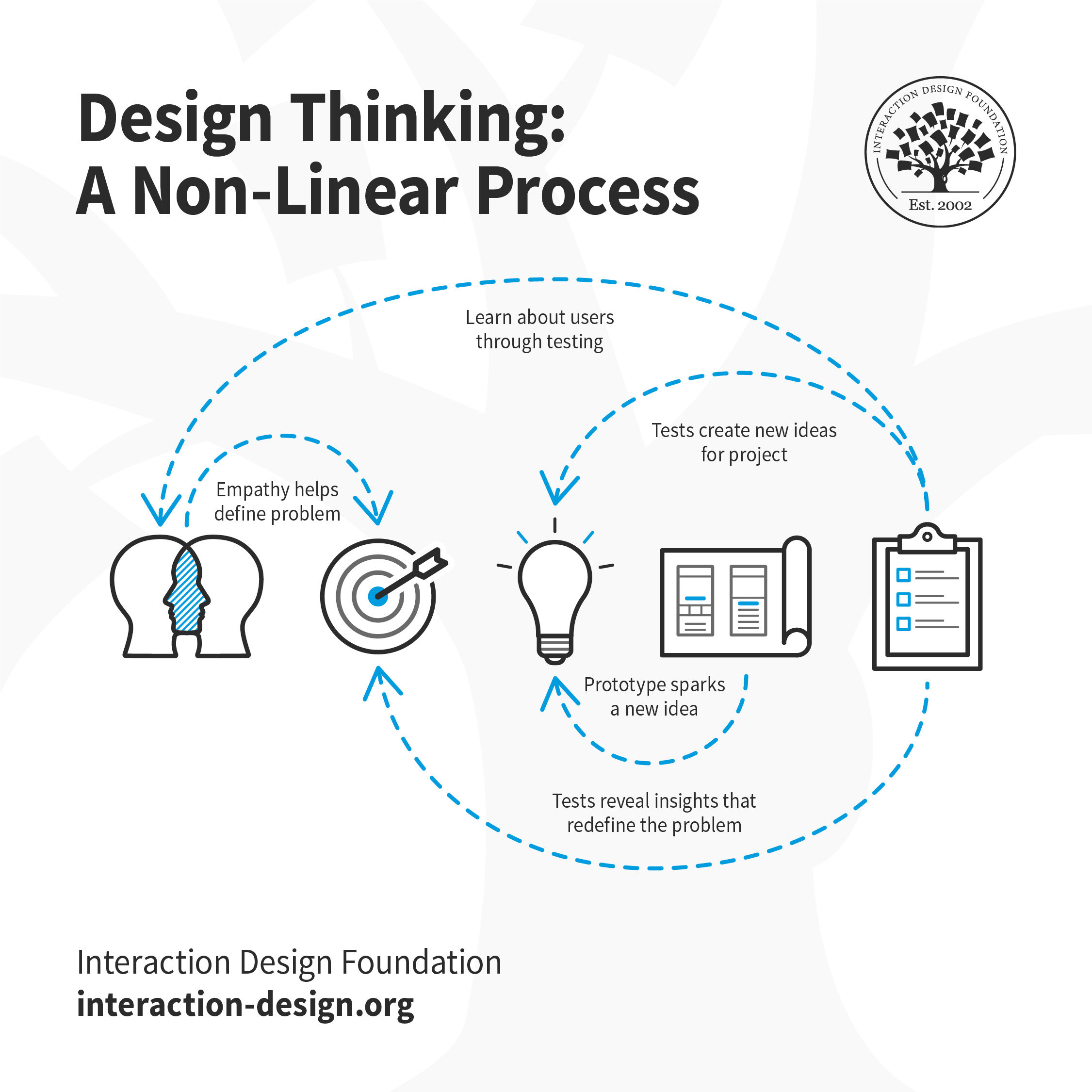
It is important to note the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes which contribute to the entire design project, rather than sequential steps. By the end of the Prototype stage, the design team will have a better idea of the product’s limitations and the problems it faces.
One study found that around 20 percent of the carbon generated by a diesel vehicle comes from its production. If the vehicle ran on only renewable energy, production emissions would account for 85 percent of the total. With more sustainable design, electric-vehicle (EV) manufacturers stand to reduce the lifetime emissions of their products significantly.
The Ultimate Guide to UX User Stories [With Examples]
The Rise of the Design Thinking Movement and its Relation to Architecture - ArchDaily
The Rise of the Design Thinking Movement and its Relation to Architecture.
Posted: Wed, 19 Jan 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
In this guide, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about the Design Thinking process—including where it comes from, why it’s so valuable, and what it’s used for. We’ll then explore the five stages of the Design Thinking process in detail. In addition, jobs that require design thinking statistically have higher salaries. Marketing manager job postings that require design thinking skills, however, have a median annual salary of $133,900—a 24 percent increase. Here are the four phases for effective innovation and, by extension, design thinking.
Establishing Empathy to Foster Customer-Centric Design
During this time, DTV efforts were groundbreaking because they were based on data rather than experience. They also reached across functions, in contrast to the typical value-engineering approach. McKinsey analysis has found that some industries—such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer product companies—have already made strides toward combining product and service into a unified customer experience. Read on for concrete examples of how companies have applied design thinking to offer innovative—and lucrative—customer experiences. And they both emphasize listening to and deeply understanding users and continually gathering and implementing feedback to develop, refine, and improve a service. There’s more to succeeding in business than developing a great product or service that generates a financial return.
You may also notice skills like agile methodology, user experience, and prototyping in job postings, along with non-design skills, such as product management, strategic planning, and new product development. Let’s now take a quick look at 10 popular frameworks to further understand this innovative and revolutionary process. We live in an era of experiences, be they services or products, and we’ve come to have high expectations for these experiences. They are becoming more complex in nature as information and technology continues to evolve.
The product research survey template is a great starting point to identify who your users are, what they think about your product, and what problems they’re having. These insights will be invaluable as you move through the design thinking process and start ideating and prototyping solutions to the most common issues affecting your users. Here at CareerFoundry, we not only teach design thinking as part of our UX Design Course, but we also incorporate it in the way we work and make decisions. The majority of our users are adult learners who are juggling online study with full-time work, and so one of the biggest challenges they face is time management. Based on the design thinking framework, we conducted extensive user research, including an in-house time management workshop with real students.
User personas are created based on observations from a variety of user surveys, interviews and analytics. As a critical piece of the Design Thinking process, user personas help teams focus all their downstream problem-solving efforts. User journeys are a powerful visualization technique that combine user personas and user stories into a complete experience roadmap. Defining the journey helps uncover new moments and opportunities to delight users and improve the user experience.
In order for this approach to be adopted across large organizations, it needed to be standardized. Cue design thinking, a formalized framework of applying the creative design process to traditional business problems. Design Thinking is not exclusive to designers—all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering and business have practiced it. User experience expert Don Norman describes human-centered design (HCD) as a more evolved form of user-centered design (UCD). The word "users" removes their importance and treats them more like objects than people.
Design Thinking workshops aren’t just for designers, though; all teams can use and benefit from this creative approach to problem-solving. Design thinking is different from other innovation and ideation processes in that it’s solution-based and user-centric rather than problem-based. This means it focuses on the solution to a problem instead of the problem itself. When a team from MIT’s Integrated Design and Management program together with the design firm Altitude took on that task, they met with walker users to interview them, observe them, and understand their experiences.


No comments:
Post a Comment